Collagen 101: Your Comprehensive Guide to Collagen Structure, Functions and Benefits
Collagen - The Framework of Our Body
The human body is a true marvel of nature. A central component that gives this marvel shape and firmness is collagen. It is the most common protein in the human body and essentially forms the framework of our skin, bones, muscles, and other structures. But what exactly is collagen, what functions does it serve, and how can we support the body in its collagen production? This report aims to provide you with a detailed insight into the world of collagen.
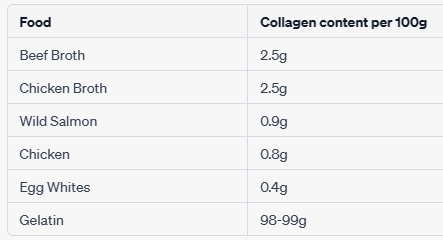
What foods is collagen found in?
Please note, while some foods contain collagen, the most effective way to absorb collagen is through the use of hydrolyzed collagen. This is a form of collagen that has been broken down into smaller peptides and is found in many collagen supplements. Hydrolyzed collagen is more readily absorbed and utilized by the body.
It's also important to note that some foods, while not directly containing collagen, are rich in amino acids that the body needs for collagen production. These include foods like lean meats, fish, eggs, beans and legumes, soy, and cheese.

Origin and Composition of Collagen
The word collagen is derived from the Greek word "Kolla," which means glue. Collagen is therefore essentially the natural "glue" of our bodies and holds different structures together. Collagen primarily consists of the amino acids glycine, proline, and hydroxyproline. There are 28 different types of collagen, each varying in structure and function.
The three most important types are:
Collagen Type I: This type makes up 90% of the body and forms the framework of skin, bones, tendons, and ligaments.
Collagen Type II: This type is mainly found in cartilage, intervertebral discs, and the vitreous body of the eye, contributing to joint and cartilage stability.
Collagen Type III: This type is found in the skin, skeletal muscle, internal organs, and arteries, among others.
How much collagen do I need daily?
The precise amount of collagen a person needs daily can vary, depending on various factors such as age, gender, overall health, and a person's specific health goals. To date, there are no official recommendations for a specific daily dose of collagen.
However, many clinical studies have reported positive effects from taking collagen in dosages ranging from 2.5g to 15g per day. Some manufacturers of collagen supplements recommend a dosage of about 10g per day for general health purposes.
It's important to note that collagen supplements are not necessary for everyone. The body produces collagen on its own, and a balanced diet rich in proteins and vitamin C can support the body's own production.
If you're considering taking a collagen supplement, talk to your doctor or a nutritionist. They can advise you and ensure that taking collagen is safe and appropriate for your individual health needs.
Functions and Benefits of Collagen
Collagen has a variety of functions and benefits for our body. It not only strengthens the bones, connective tissue, tendons, ligaments, and cartilage but also has positive effects on the health of our skin, hair, and nails. Collagen aids in wound healing and regeneration after injuries and can help minimize age-related inflammation and pain. Furthermore, collagen can contribute to maintaining bone density and reducing the risk of atherosclerosis by regulating cholesterol levels in the blood. The contained amino acid glycine can also help stabilize blood sugar levels.
Aging Process and Collagen
As we age, the body's own production of collagen begins to decrease. This process starts around the age of 25 and results in our body producing about 1.5% less collagen each year. This decline can manifest through a variety of symptoms such as sagging, dry skin, joint pain, or gastrointestinal problems.
Preventing Collagen Deficiency
The good news is that there are ways to slow down collagen degradation and support the body in its collagen production. Here are some tips:
Ensure adequate intake of Vitamin C: Vitamin C is essential for collagen production. Therefore, you should ensure that you consume sufficient Vitamin C-rich foods or use a suitable dietary supplement if necessary. Avoid stress and ensure enough sleep: Stress and lack of sleep can impair collagen production. Therefore, try to reduce stress and ensure you get enough sleep. Reduce the consumption of sugar and simple carbohydrates: Too much sugar in the body can cause sugar to bind to the structure proteins collagen and elastin in the connective tissue, hardening them. This causes these proteins to lose their support function, which can lead to skin sagging and wrinkle formation. Avoid excessive sun exposure: UV rays can accelerate collagen degradation and are responsible for a large part of visible skin aging. Always use suitable sun protection.
How to Best Supplement Collagen?
Supplementing collagen can occur in a variety of ways, depending on individual preferences and lifestyles. Here are some methods:
Collagen Powder: This is a very common method of supplementing collagen. The powder can be stirred into beverages like water, juices, smoothies, or coffee. It's typically flavorless and dissolves well in liquids.
Collagen Capsules: Collagen can also be consumed in capsule form. This might be a good option for those who prefer a quick and convenient intake method.
Collagen-Rich Foods: Bone broth is a natural food rich in collagen. It is produced by the long-term boiling of bones and connective tissue, which releases collagen. Certain types of fish and meat also have high collagen content.
Collagen Drinks: There are various pre-made drinks on the market containing collagen. These could be a convenient option for those frequently on the go.
Topical Collagen Creams: Although the effectiveness of topical collagen creams is debated (since collagen molecules might be too large to effectively penetrate the skin), some individuals prefer this method of collagen supplementation.
Regardless of the method you choose, remember that maintaining a healthy diet and lifestyle is equally important. Consume a variety of protein-rich foods and Vitamin C, as these nutrients are vital for collagen production. Avoid excessive sun exposure and smoking, as these factors can accelerate the breakdown of collagen in the skin.
It's also crucial to note that although collagen supplements are generally considered safe, they can cause side effects such as upset stomach and allergic reactions. If you're considering supplementing collagen, first consult with your doctor or a dietitian. They can help determine whether collagen supplements are suitable for you and what dosage is optimal.
In conclusion, collagen is an essential building block of our bodies and serves a multitude of functions. With the right measures, everyone can contribute to maintaining the health and youthfulness of their body and getting the most out of their collagen household.








